Safari Keychain Woes
July 29th, 2011I’ve been running OS X Lion for a long time and generally enjoying it. But at some point along the line, Safari 5.1 stopped correctly inserting my keychain passwords into forms for me.
For the longest time, I assumed it was simple mistakes: I had neglected to ever approve “remember this password,” or I had somehow invalidated the password in my keychain. But recently I have come to realize that Safari is no longer auto-filling passwords for me on any site. Ever. This sucks. Usually when something like this happens, the first thing I do is “Repair Keychain” from the Keychain Access application. But in this case, the keychain is reportedly not damaged. No help.
To research this problem, I started the way I usually do: Googling it. While there are many promising search results, most of them lead to “solutions” that are not applicable to my scenario. Most commonly it seems the user has somehow ended up with the appropriate “User names and passwords” checkbox being turned off in Safari’s AutoFill preferences.
So how does a programmer like myself approach a problem like this? In recent years, Apple’s Instruments application has become an incredible asset for tracking down weird behavior not only in my own apps, but in other apps and in the system itself. I opened it up and started a new “Time Profiler” instrumentation session, targeting Safari. I know that Safari used to autofill my password whenever I typed in an account name that it recognized, so I start Instruments “sampling” Safari while I type my PayPal account name into the PayPal login page, and stop it after I’m done.
I want to figure out where Safari is failing to get my password, so I take a wild leap and assume the corresponding function call in Safari contains the word “password.” Typing this into the Instruments search box yields promising results:

Now I know that Safari is at least making an effort to fetch the corresponding password for me. I see that it’s calling -[NSURLCredential password], which in turn calls a lower-level Keychain Services function, SecItemCopyMatching(). But why isn’t it filling in my password?
At this point I switch to gdb, where i can attach to the running instance of Safari and dig a little deeper into the issue.
% gdb (gdb) attach Safari (gdb) b -[NSURLCredential password] Breakpoint 1 at 0x7fff8ddff4af (gdb) c Continuing.
I know from Instruments that Safari will call this method when it tries to autofill my password, so I go back to Safari and enter my PayPal ID again. Sure enough, Safari “freezes” indicating that gdb has interrupted it where my breakpoint was set. Now, I realize this isn’t for the faint of heart, but you can use gdb to effectively debug an application, even if you don’t have the source code. You just have to know a bit about how Apple’s compiler translates source code into corresponding assembly language instructions, and where the arguments are placed when calling methods.
Breakpoint 1, 0x00007fff8ddff4af in -[NSURLCredential password] () (gdb) d Delete all breakpoints? (y or n) y (gdb) po $rdi <NSURLCredential: 0x7ffd34d62920>: [email protected] (gdb) po [$rdi password] 2: x/i $pc 0x7fff9192760e <gdb_class_getClass+4>: mov 0x20(%rdi),%rax Can't print the description of a NIL object. (gdb) (gdb) p (int) [$rdi hasPassword] $11 = 1
What I’ve done here is first delete the breakpoint, so I don’t get interrupted while poking around from gdb itself. Then, I display the NSURLCredential object’s description, confirming it corresponds to the account I’m trying to log into. Finally, I call the password method on this NSURLCredential object myself, so I can see quickly and easily what the response will be. Gdb’s objection to trying to print a NIL object confirms that the password is not being returned. I am further able to confirm with NSURLCredential’s “hasPassword” method that the keychain does have a password for this account, but it isn’t being returned.
Here we have a situation where apparently Safari is trying to get my password, but the system is vexing it. Let’s confirm by setting a breakpoint a little deeper, at the Keychain Services level that we also noticed in Instruments.
(gdb) b SecItemCopyMatching
Breakpoint 3 at 0x7fff85919582
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Breakpoint 3, 0x00007fff85919582 in SecItemCopyMatching ()
(gdb) po $rdi
{
acct = "[email protected]";
atyp = form;
cdat = "2007-06-02 16:17:01 +0000";
class = inet;
desc = "Web form password";
icmt = default;
labl = "www.paypal.com ([email protected])";
"m_Limit" = "m_LimitOne";
mdat = "2011-07-29 15:30:15 +0000";
port = 0;
ptcl = htps;
"r_Data" = 1;
srvr = "www.paypal.com";
}
So far, so good. It looks like NSURLCredential is properly passing a set of criteria to the keychain, describing the kind of password item it’s looking for. I take a peek at the second argument to SecItemCopyMatching, which is a pointer to where the result will be stored, and then I ask gdb to continue executing until the function is complete.
(gdb) x/x $rsi 0x7fff62eb3590: 0x0000000000000000 (gdb) fin Run till exit from #0 0x00007fff85919582 in SecItemCopyMatching () 0x00007fff86417c29 in URLCredentialInternetPassword::copyPassword ()
When gdb returns control to me, I know the function has finished calling, so I examine the result area in memory.
(gdb) x/x 0x7fff62eb3590 0x7fff62eb3590: 0x0000000000000000
Indeed, it’s NULL! What is going on, here? I decided to dust off my Usable Keychain Scripting tool, which makes it easy to use AppleScript to search and inspect the keychain. Is the inability to access the password a system-wide thing, or just something that is vexing Safari?
tell application "Usable Keychain Scripting" tell current keychain password of keychain item "www.paypal.com ([email protected])" end tell end tell
The script works perfectly, first causing the system to ask permission to authorize “Usable Keychain Scripting” to access the keychain item, and then returning the expected password string. This got me thinking, is it possible I’ve somehow got Keychain Accessing refuse access only to Safari?
When I look at the “Access Controls” for the affected keychain item, it lists Safari as one of the permitted apps. What the hell, I think. I’ll remove it from the list, and then re-add it. To try to “dislodge” something. Confoundingly, everytime I try to add it, it just silently fails to appear in the list. I am able to add any other app without an issue.
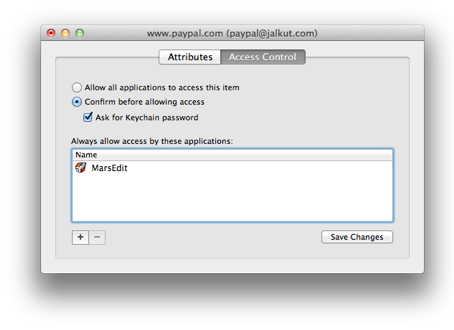
As a quick check, I change the setting to “Allow all applications to access this item,” and save the changes. When I return to Safari and type in the login name, it instantly fills in the password for me.
My system has a functional keychain but Safari seems unable to be authorized to access it, either on a one-time basis or as a “always allow” permission. I finally got the clever idea to look at /var/log/secure.log, which frankly, I should have done about 5 hours earlier. What’s this?
com.apple.SecurityServer[33]: suppressing keychain prompt for invalidly signed client /Applications/Safari.app(2938)
Aha! So that would explain it. Funny, I don’t remember tweaking anything inside the Safari application bundle, but this is certainly a very real example of how a broken code signature on Mac OS X can cause extremely subtle, hard to track-down “bugs.” I re-signed the applicaton on my own:
codesign -f -s - /Applications/Safari.app
When I reopened the app, and went to PayPal’s site, voila! It prompted me for permission, I approved, and now everything is back to normal.
I examined the Safari.app bundle contents to try to remember what I might have tweaked. Then my memory was jogged. I had opened and edited Safari’s Info.plist file to play around with some settings. Don’t ask, it’s an even longer story than this.
I take full responsibility for getting myself into this mess. I’ll certainly be more careful in the future to consider the implications of breaking code signatures on apps. However, I do think that the failure behavior could have been more informative. That NSLog I found in the console about refusing to prompt the user because of a broken code signature, could have been presented as a dialog that would instantly inform the user something is fishy. If my copy of Safari actually had been compromised by a nefarious individual, I wouldn’t have thought twice about continuing to enter my passwords and trying my damnedest to get Keychain to share my passwords with the compromised application.

